We would like to inform you that it is now possible to pay for orders by credit card again. We are using a new service provider. We apologise for the inconvenience.

Free Shipping
Dear customers
We’re letting you know that our free shipping limit has increased. Previously, it was from €70, but now it is from €100. We have tried to keep the free shipping limit as low as possible. Unfortunately, however, transport companies have recently increased their prices a lot. So we eventually had to do it too. Nevertheless, we hope that you will find the right products in our e-store and we will try to offer discounts and campaigns more often in the future.
Enhancetech team

Unveiling the Power of Ligandrol LGD-4033
A Deep Dive into its Impact on Muscle Mass
In the ever-evolving world of fitness and bodybuilding, enthusiasts are constantly on the lookout for supplements that can provide an edge in achieving their physique goals. One such compound that has gained attention in recent years is Ligandrol LGD-4033. Marketed as a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM). LGD-4033 has sparked interest for its potential impact on muscle mass. In this blog post, we will explore the effects of Ligandrol on muscle mass and delve into the science behind its mechanism of action.
Ligandrol LGD-4033
Ligandrol, also known as LGD-4033, is a synthetic compound design to mimic the effects of testosterone. Unlike traditional anabolic steroids, which can have a broad spectrum of effects on various tissues. It is purport to selectively target androgen receptors in muscle and bone cells. This selectivity is what sets SARMs apart and contributes to their potential as performance-enhancing compounds.
Effects on Muscle Mass
Muscle Protein Synthesis (MPS):
One of the primary mechanisms through which Ligandrol is believed to influence muscle mass is by increasing muscle protein synthesis. MPS is the process by which the body builds new muscle tissue. The activation of androgen receptors in muscle cells can potentially enhance this crucial aspect of muscle growth.
Anabolic Activity:
It is often lauded for its anabolic properties. It mean that it has the potential to promote the growth of muscle tissue. Users report an increase in lean muscle mass. Which is particularly appealing for those aiming to improve their body composition.
Preventing Muscle Wasting:
It has also been studied for its potential in preventing muscle wasting conditions. Also some research suggests that it may be useful in preserving muscle mass during periods of caloric deficit or catabolic stress. Such as during intense training or when recovering from an injury.
Scientific Studies and Research
While the evidence from users is positive. It’s essential to acknowledge that the scientific understanding of substance is still in its early stages. Although limited clinical trials have been conducted. Also more research is needed to fully elucidate its long-term effects, safety profile, and potential side effects.
Potential Side Effects
It’s crucial to note that, like any performance-enhancing substance, it may have potential side effects. These can include hormonal imbalances, suppression of natural testosterone production, and other adverse effects. Anyone considering the use of ligandrol should consult with a professional and carefully weigh the potential risks against the benefits.
Substance has emerged as a promising compound in the realm of muscle growth and body composition improvement. While users often report positive results, it’s essential to approach its use with caution and prioritize health and safety. As research continues to unfold, the fitness community will gain a more comprehensive understanding of Ligandrol’s impact on muscle mass and its role in the pursuit of physical excellence.

The Power of Physical Activity
In our fast-paced world, where hectic schedules and sedentary lifestyles have become the norm, prioritizing our health has never been more crucial. Incorporating regular exercise and healthy activities into our daily routines is a powerful way to boost both physical and mental well-being. In this blog post, we’ll explore the numerous benefits of engaging in healthy activities and exercise. Also how they contribute to a vibrant and fulfilling life.
Physical Health Benefits
Regular exercise is the cornerstone of a healthy lifestyle. From improving cardiovascular health to enhancing muscle strength and flexibility, physical activity offers a myriad of benefits. It helps to maintain a healthy weight, reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and diabetes, and promotes overall longevity. Whether it’s brisk walking, jogging, cycling, or strength training. Finding an activity that suits your preferences and fitness level is essential.
Mental Well-being
The connection between physical activity and mental health is undeniable. Exercise releases endorphins, the body’s natural mood lifters, which can alleviate symptoms of stress, anxiety, and depression. Engaging in regular physical activity also promotes better sleep, cognitive function, and helps manage overall mental well-being. Consider activities like yoga or mindfulness exercises to combine physical movement with mental relaxation.
Social Engagement
Many healthy activities involve social interaction, fostering a sense of community and support. Joining group fitness classes, sports leagues, or recreational clubs not only provides an opportunity to stay active. But also allows for the development of meaningful social connections. The camaraderie and shared goals create a positive and motivating environment.
Variety is the Spice of Life
One of the keys to sustaining a healthy lifestyle is variety in physical activities. Mixing up your routine not only keeps things interesting but also ensures that different muscle groups are engaged. Try a combination of aerobic exercises, strength training, and flexibility exercises to achieve a well-rounded fitness routine. Hiking, swimming, dancing, and even gardening are excellent options to add diversity to your activities.
Incorporating Exercise into Daily Life
Finding time for exercise in a busy schedule can be challenging, but it’s not impossible. Simple changes like taking the stairs instead of the elevator, walking or cycling to work, or scheduling short, intense workouts during lunch breaks can make a significant difference. The key is to make physical activity a non-negotiable part of your routine.
Setting Realistic Goals
Establishing achievable fitness goals is essential for long-term success. Whether it’s completing a 5K run, mastering a challenging yoga pose, or consistently hitting the gym, setting realistic and measurable goals helps maintain motivation and track progress. Celebrate small victories along the way to stay motivated and focused on your health journey.
Incorporating healthy activities and exercise into your daily life is a powerful investment in your overall well-being. The benefits extend beyond the physical, positively impacting mental health, social connections, and overall quality of life. Whether you’re a fitness enthusiast or just starting your wellness journey, remember that every small step towards a healthier lifestyle counts. So, lace up those sneakers, find an activity you enjoy, and let the journey to a healthier, happier you begin.

Black Friday Sarms Sale
Dear valued regular and new customers!
We have happy to say that we have massive discounts. Up to 35% discount for all our provided SARMs and Nootropics. Black Friday Sale lasts november 24-26 because we consider with different time zones, and we want all our customers to take part in the discounts. No matter what part of the world they live in. Go to our store and take advantage of the good opportunity to purchase SARMs.
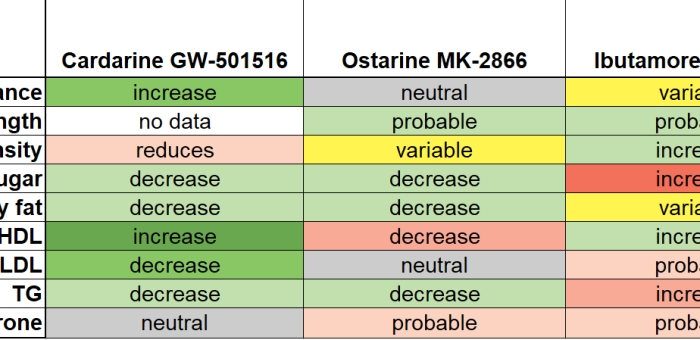
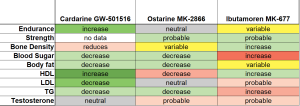
SARMs Comparison table
Cardarine, Ostarine and Ibutamoren are very different performance-enhancing research chemicals SARMs. All three have been moderately well researched.
Cardarine increases endurance and lipid metabolism. I´ts microdose elevates good cholesterol.
Ostarine mimics the anabolic effects of testosterone more selectively than anabolic steroids. It´s relatively non-toxic; alas, users of high doses have been hospitalized due to adverse effects similar to anabolic steroids (liver toxicity).
Ibutamoren is a synthetic analogue of hunger hormone. That alters the intensity rather than pattern of growth hormone secretion.
Larger doses have probably higher risk of adverse effects. Recently, it was even suggested that cardarine is dangerous when combined with a SARM (ostarine). While it may tempting to think that cardarine would be a good means to reduce the side effects of SARMs or ibutamoren, it may be a bad idea. Recently, it was suggested that combination of cardarine and ostarine is toxic. At least after prolonged use of the combination. The following table shows both desirable and undesirable effects of these three major performance-enhancing chemicals.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19852734/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31642815/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9467542/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18981485/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10372705/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9329386/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22814748/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14525954/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25854303/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17110604/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34678947/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20602678/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32876707/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29785666/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22031847/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24708238/
What kind of performance enhancers are PDE-5 inhibitors?
Phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE-5) inhibitors were originally investigated for hypertension because of their ability to relax blood vessels. To researchers’ surprise, inhibiting PDE-5 was even better for improving male erection. That’s why PDE-5 inhibitors such as sildenafil or tadalafil are most commonly marketed for improving erectile function. Relaxing blood vessels may be beneficial for purposes of exercise. PDE-5 inhibitors have potential to increase endurance performance because it counteracts contraction of blood vessels in lungs [1].
Clinical studies have shown that sildenafil and tadalafil can improve exercise capacity in certain patient populations. A proof-of-concept study demonstrated somewhat increased aerobic exercise capacity in young adult patients with cystic fibrosis, a disease that reduces lung function [2]. 25 mg of sildenafil increased the VOmax approximately 5% after four weeks of use while a single 50 mg dose failed to increase VOmax significantly despite some tendency to do so. There is some data that tadalafil increases exercise capacity of patients with pulmonary hypertension . It must be noted that the study subjects were those who could not walk 4.5 km/h for 10 minutes [3] and about third of the patients suffered from headache as an side effect.
In diabetic but not in healthy women, tadalafil has been shown to increase glucose utilization in the muscle [5]. In cyclists, sildenafil did not improve the results in the context of 16.1 km exercise [1]. On the negatice side, tadalafil is associated with yet unexplained higher incidence of back pain in clinical studies. About 8.3% to 9.4% of men taking tadalafil suffered from back pain while only 3.4% of men in placebo group suffered from back pain — the risk is greater than two-fold [6]. There was no difference in blood parameters. Hence, the increased incidence of back pain lacks explanation. One might ask if the back pain is associated with increased strenuous sexual performance. Anabolic steroid users seem to use PDE-5 inhibitors mainly for sexual enhancement also [7]. In mice, PDE-5 inhibitors can increase the production of testosterone [8].
In men – possible but unlikely. The scientific consensus based on several human studies is that PDE-5 inhibitors do not increase testosterone production. PDE-5 inhibitors are beneficial for semen but, again, in infertile rather than healthy men [9]. It seems unlikely that PDE-5 inhibitors augment testosterone. It is the other way around, instead [10]. PDE-5 inhibitors are sexual performance enhancers that just happen to be performance enhancers in serious lung disease patients.
Don´t hesitate to ask it.
[1] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30653578/
[2] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31803404/
[3] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19470885/
[4] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/4377045/
[5] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20535445/
[6] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16034469/
[7] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31303195/
[8] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19659904/
[9] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28259808/
[10] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24251448/
Michael’s feedback
Hi Enhancetech
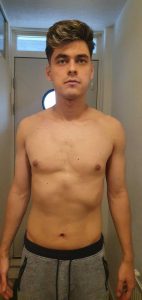
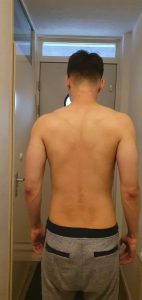
Here’s a picture of me taken 2 months between this summer. In this period I used cardarine and ostarine. I combination with 2/4 protein, 1/4 carbs and 1/4 fats I felt the shredding process even after a few days. Luckily, as you can see, I had noticable gains in muscle size too.
Great products which I will use over and over again! Very pleased.
Kind regards,
Michael

Igor Buracof feedback
Hello everyone
I would like to share my personal experience with SARMS to be more precisely the experience was only with SARMS made from enhancetech.
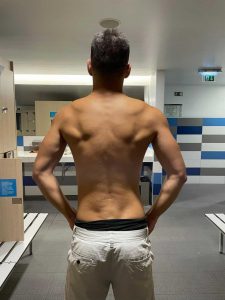
I started to take SARMS around 20/nov/2020. In the beginning I was bulking and it gave me a lot of strength, stamina and power during the workout session, I was into and RAD140, LGD-4033 and YK11 .
Then I moved to cut using MK-677 and RAD140. Was around 80 days with this cycle and it worked greatly. I would like to share bellow my before and after picture.
Igor Buracof
Igor on the beach today
BEFORE
AFTER